As a leading platform vendor in the Business Process Automation (BPA) space, we've witnessed the transformative power of BPA firsthand. From boosting efficiency to streamlining operations, the benefits are undeniable. We've gathered inspiring success stories from enterprises that have unlocked the full potential of BPA.
In this comprehensive guide, you'll explore:
- The evolution of Business Process Automation
- Types of automation
- Critical differences of BPA and Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
You'll also discover
- The most and least automatable processes
- The tools, use cases, and benefits of BPA.
But that's not all.
We've included a section for frequently asked questions (FAQs) to answer your questions.
Join us on a journey of discovery and unlock the true potential of Business Process Automation. By the end, you'll have a solid understanding and the confidence to take your business processes from nascent to mature.
What is Business Process Automation (BPA)?
Business process automation (BPA) means using software to automate manual and repeatable business processes. BPA solutions are generally complex, connected to multiple enterprise information technology (IT) systems, and custom developed by in-house business and IT teams specifically to the requirements of an organization.
We emphasize that using BPA software to automate simple tasks is overkill because you can automate simple departmental tasks/workflow with task-automation SaaS (Software-as-a-Service) solutions.
For more complex processes, analyst firm Gartner recommends that firms should use BPA platforms to automate business processes that are:
- Event-driven
- Mission-critical
- Core processes
For example, you can easily automate activities like approving/assigning tasks and querying a database using a point solution (a single use-case SaaS app). However, enterprise BPA software is a better alternative if your company operates on a larger scale with operations across multiple territories/countries with complex processes and dynamic process logic to achieve business outcomes.
We begin with the evolution of BPA to understand the context of using BPA tools.
Evolution from ERP to BPM to BPA
Business Process Automation has evolved from multiple technologies. Starting from Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP), Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), and Business Process Management (BPM), we have reached BPA (and a much-restricted variant called Robotic Process Automation). Historically, a common objective has been optimizing business processes as executives consider these processes their lifeblood. The result was the development of different methods and technologies to optimize and transform operations.
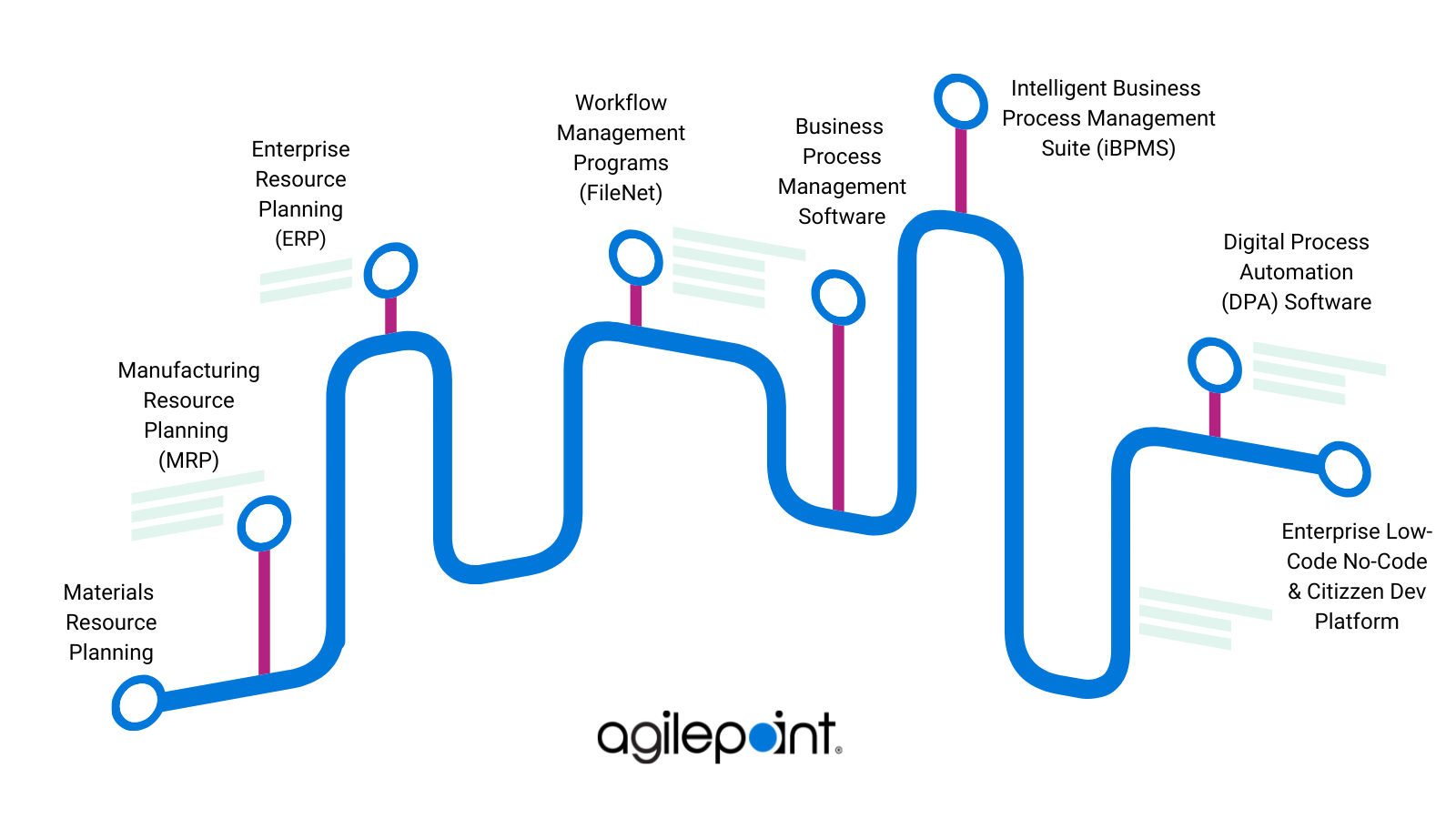
You need to consider the context of your automation project before deciding on the type of BPA tool appropriate for your firm. For instance, if it's document-heavy workflows that you want to automate, it's better to start your evaluation from tools that are for document and content automation. If your workflows are spread across multiple departments, it is better to approach the RFI (Request for Information) process by shortlisting enterprise BPA tools.
Below we describe four types of Business Process Automation.
Types of BPA
There are different types of Business Process Automation that you can use according to your desired business objectives, such as:
1. Task Automation
Task automation uses single-use apps to perform repetitive tasks and activities without human intervention. Three common examples are automating appointment scheduling, sending automated email replies, and creating a new ticket from an email or form. Essentially, it's a way to streamline and simplify the tasks you need to do daily, saving you time and energy. Although you can use task-specific software to automate a single type of task, for instance, appointment scheduling via Calendly or Google Calendar, there are task-agnostic software like Zapier, IFTTT, and Power Automate to automate tasks.
Single-Purpose Task Automation Software
Calendly, Google Calendar, JitBit
Task-agnostic Automation Software
Zapier, IFTTT, Power Automate
2. Workflow automation
Workflow automation is the process of automating multiple tasks to streamline and automate the activities involved in a specific business process. Organizations use workflow automation tools to eliminate repetitive, manual, and error-prone tasks, improve efficiency, and increase productivity. You can use these automation tools to manage and track tasks, approvals, and communications within a team or organization.
Single Function Workflow Automation Software
CRM, Project Management Software, Ticketing System (e.g., HubSpot, Zoho, Asana, ClickUp)
Multi-Function Workflow Automation Software
Office Suites, ERPs, Power Platform (Monday.com, Office365, SAP)
3. Document automation
Document automation uses technology to automate tasks and workflows to create electronic documents. You can use document automation software to automatically create, manage and distribute documents. Three common examples are:
- Generating documents such as contracts, invoices, and reports.
- Preparing document templates.
- Approving documents automatically and accurately.
A document automation tool consists of a template feature and workflow capabilities to populate fields with data from other systems automatically. You may use it for automating document-heavy processes.
Types of RPA
Attended, Unattended, and Hybrid RPA
Common RPA Tools
RPA Blue Prism, UiPath, Automation Anywhere
4. Robotic process automation
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a technology that can enable you to automate repetitive, manual, and rule-based business processes by using software robots, also known as "bots" or "digital workers."
These bots are programmed to mimic the actions of a human worker. The simple tasks may be to navigate through applications, input data, or generate reports. RPA can help you to improve efficiency, reduce errors, and lower costs by automating these tasks.
Additionally, you can integrate RPA tools with other technologies such as iBPMS Suites, Artificial Intelligence, and Machine Learning to enhance the capabilities of your automation process.
5. Cross-functional Process Automation
Cross-functional process automation, also called Intelligent Automation, is among the most prized forms of business process automation. It is the automation of complex, multi-function, and long-running processes that span across ERP and CRM systems, RPA, homegrown IT systems, and humans. These systems combine BPM modules, AI+ML capabilities, system integration, and application development features.
Another way to understand cross-functional process automation is that these tools combine the functionalities of process, workflow, and document automation and provide tooling for application dev and integration with 3rd party systems (like ERPs, CRMs, and Legacy Systems).
Cross-Functional Automation Software
ServiceNow, TrackVia, Kissflow,
Enterprise-oriented Cross-Functional Automation Software
AgilePoint, Pega, Nintex, Bizagi
The categorization mentioned above is just one way to look at BPA tools during your evaluation process. It does not limit a particular tool/vendor. Instead, it helps to help contextualize the appropriate use of different types of tools. It’s also possible that one tool may neatly handle needs across multiple automation types.
As another way to comprehend what processes to automate, we have compiled a list of the most and least automatable processes below.
Most Automatable vs. Least Automatable Business Processes
There’s an influx of automation technologies, and it gets challenging to get one’s head around the type of processes you should automate and the technology platform suitable for the automation of each process group.
Below is a list of the ten most and least automatable process groups. The classification is based on work done by IBM Institute for Business Value research and the American Productivity and Quality Center (APQC).
Most Automatable Business Processes
- Process accounts payable and expenses
- Process payroll
- Perform global trade services
- Perform revenue accounting
- Deliver/support information technology services
- Manage customer service contracts
- Manage product recalls and audits
- Evaluate customer service and satisfaction
- Produce, manufacture and deliver product
- Manage logistics and warehousing
- Reward and retain employees
Least Automatable Business Processes
- Dispose of assets
- Deploy information technology solutions
- Develop knowledge management capabilities
- Manage employee relations
- Manage business resiliency
- Develop customer service strategy
- Generate and define new product/service ideas
- Redeploy and retire employees
- Establish service delivery governance strategies
We’ve got our head around Business Process Automation and the context of using BPA tools in your digital transformation initiatives. We now dive into a term called Robotic Process Automation, or RPA, and the difference between BPA and RPA.
Difference between BPA and RPA
RPA is neither related to factory automation nor industrial robots (or robotic machines) to perform production tasks, and it is much simpler and breaks easily.
RPA uses software bots to automate repetitive and static tasks by mimicking a knowledge worker's keystrokes and mouse clicks. A critical difference between Business Process Automation (BPA) and Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is that BPA is a much broader and more effective approach to automating multiple workflows of an end-to-end process.
For instance, the type of tasks RPA is meant to automate include reading a document or retrieving data from a system. Below we share a few examples of tasks teams would automate using BPA and RPA.
Examples of BPA (Business Process Automation)
- Automate the invoicing process by integrating it with finance management software.
- Implement a CRM system to automate customer relationship management tasks.
- An electronic HR system to automate HR processes such as employee onboarding, performance management, and benefits administration.
Examples of RPA (Robotic Process Automation)
- Automate data entry tasks by using software bots to extract data from invoices and populate an accounting system.
- Automate the processing of customer orders using software bots to extract information from customer emails and input it into a fulfillment system.
- Automate the reconciliation process in a banking system using software bots to match transactions and resolve discrepancies.
Another way to understand the difference between BPA and RPA is to go through examples of both in the same organizational function. Let’s take the example of logistics.
Business Process Automation in Logistics
- BPA can help you to automate the purchase order management system by integrating the whole workflow with suppliers, reducing manual data entry, and improving accuracy.
- As a procurement or fulfillment executive, BPA can help you in monitoring inventory levels, order fulfillment, and delivery performance through dashboard reporting and analytics.
Robotic Process Automation in Logistics
- As a finance executive, RPA can help you to automate data entry tasks by using software bots to extract data from invoices and populate it in your accounting system.
- Your inbound logistics department or customs clearance brokerage firm can use software bots that perform document preparation and data validation.
Let’s circle back to BPA and the different type of BPA tools that you may consider for your automation initiatives.
BPA Tools
There are 100s of BPA tools in the market. Three critical aspects of a BPA tool for large companies are:
- Breadth of use cases
- Depth of technical feature set (related to application dev, process automation, and integration)
- Governance capabilities of the Business Process Automation (BPA) platform
Gartner categorizes BPA tools into four categories:
- Dynamic Case Management (DCM)
- Intelligent Business Process Management Suites (iBPMS)
- Process Mining
- RPA (Robotic Process Automation)
Another prominent technology research and analyst firm Forrester categorizes BPA tools into three categories:
- Digital Process Automation (DPA) Platforms
- DPA Wide
- DPA Deep
- Dynamic Case Management (DCM)
- RPA (Robotic Process Automation)
Refer to Forrester’s Wave report that lists the 14 DPA providers that matter the most. In summary, Forrester recommends enterprises “look for [low-code development platforms] that:
- Elegantly address both data-centric and process-centric development patterns
- Provide tools suitable across a range of dev personas
- Meet specific infrastructure, architecture, and dev process requirements
No explanation is complete without examples and use cases of the technology. Below we list a few use cases you can automate using mature BPA platforms.
Use Cases
Order-to-Cash
You can use a BPA platform to automate and streamline the Order to Cash process (O2C), reducing manual effort, improving the accuracy of the whole process, and reducing the risk of errors. The process consists of several stages: order placement, order processing, invoicing, and payment collection. A modern BPA platform can help you to model the process, digitize it, automate the workflows, and integrate with CRM and accounting software, to ensure data consistency and accuracy. And monitor and optimize the process.
Procure-to-pay
Procure-to-pay (P2P) is a crucial business process to gain end-to-end visibility of the process, save costs, and improve supplier relationships. Critical phases of this process include procurement, invoicing, and payment processing. You can automate the process and build use-case-specific procurement apps like return order management, order cancellation management, and procurement approvals. The BPA platform also helps to integrate this data with your ERP and accounting software to ensure data consistency.
Onboarding
The onboarding process is an essential component of customer and employee experience management. The process is especially crucial for large companies as they have multiple personas for whom they need an intuitive onboarding process.
Ultimately, automating the onboarding processes of your firm increases the longevity of business relationships.
The BPA platform provides capabilities like:
- Workflow automation to streamline and standardize the onboarding process
- Document management and e-signature to store and manage onboarding forms and agreements securely
- Communication and collaboration tools to facilitate communication between all parties involved in the onboarding process
- Reporting and analytics to track the progress of onboarding and identify areas for improvement
- Integration with HR (HCM) systems to seamlessly transfer data and automate manual tasks
AgilePoint customers use the platform to build multiple onboarding apps, from simple to more complex. For instance, a government agency using a contract onboarding app for its different departments to participate in capturing the contract details, awarding, executing the contracts, reviewing the contract, collaborating on the contract documents, obtaining a signature on contract documents, triggering the recruitment process, and sending invoices to the customer.
Benefits and goals serve as the north star of your automation projects. Below we list the key benefits of business process automation.
Benefits of BPA
You can use a BPA platform for many use cases. However, the benefits you may derive depend on the initiative's objectives. For instance, a team may choose one or more of the following business objectives and use BPA to support the goal.
- Enhance Process Efficiency
- Increase Productivity
- Improve Collaboration
- Save Costs
- Unlock revenue-earning opportunities
1. Improved Process Efficiency: BPA platforms automate and streamline complex business processes, reducing the need for manual intervention and minimizing errors. For example, in a manufacturing company, BPA can automate the production line, reducing the time required for each step and increasing overall efficiency.
2. Increased Productivity: Automated processes free up valuable time for employees to focus on more critical tasks. In a healthcare organization, BPA can automate the scheduling and appointment reminders, freeing up time for front-line staff to provide better patient care.
3. Better Data Management: BPA platforms provide centralized data management, making accessing and analyzing information in real-time more accessible. In a government agency, BPA can automate the reporting process, making it easier for analysts to access and interpret data to make informed decisions.
4. Enhanced Customer Experience: Automated processes can improve the customer experience by reducing response times, improving accuracy, and providing real-time updates. For example, in a financial services organization, BPA can be used to automate loan processing, reducing the time it takes to approve a loan and improving the customer experience.
5. Compliance and Security: BPA platforms provide a secure and auditable record of all business processes, ensuring compliance with regulations and reducing the risk of errors. For example, BPA can automate the supply chain process in a pharmaceutical company, ensuring you can track and monitor all products to meet regulatory requirements.
We need success stories and implementation scenarios to convince ourselves and others in the team whether or not a platform or type of technology is right for our firm.
Below we share three success stories from AgilePoint customers. It is a sample of 100s of success stories from our project portfolio. You may refer to other success stories published by competing vendor platforms or analyst firms covering the BPA market.
Enterprise Success Stories
It’s essential to map a BPA platform’s capabilities to your project objectives. For instance, enterprise-grade digital process automation is better suited if you plan to implement an organization-wide automation initiative. However, a SaaS app that narrowly solves a specific challenge is suitable if your automation initiative is limited to a single department or use case.
Below we have listed three enterprise success stories where large enterprises used AgilePoint:
- Defense Firm Decreased average purchase order processing time from 28 Days to 2.3 Days!
- Eneco uses Process Automation to Keep Pace in a Rapidly Evolving Energy Landscape.
- GVTC Communications Gains New Competitive Edge using AgilePoint Process-Centric Applications
Frequently Asked Questions
What type of BPA platform is suitable for medium to large enterprises?
Medium and large enterprises have more complex automation needs. Therefore, look for BPA platforms that help you fulfill data- and process-centric application development needs. As a large company, your needs may range from spreadsheet replacement to core modernization and tactical to more complex process orchestration. Additionally, you should prefer BPA platforms that offer flexible deployment options and easily integrate with other enterprise systems (both on-premise and cloud-based).
How does AgilePoint stack against other BPA platforms?
The short answer is that it depends on your team’s needs. If you prefer a platform that offers both data-centric and process-driven applications in one platform, AgilePoint is suitable for both. While there are reputable BPA platforms that you might evaluate in your digital transformation journey, we’ve mostly served customers who value governance tooling, defendable return over investment, and vendor responsiveness.
To quote from one of our Fortune 100 customers, “AgilePoint is extremely responsive and collaborative when considering requests for product enhancements.” In a nutshell, we move quickly and functionally punch above our weight.
What is the difference between RPA and BPA?
RPA (Robotic Process Automation) is a subset of BPA (Business Process Automation) that focuses explicitly on automating simple tasks like data entry and screen scraping. AgilePoint integrates with popular RPA platforms (like UiPath, Automation Anywhere, Power Automate, and Blue Prism) to help organizations overcome the challenges of low ROI from their RPA investments.
By augmenting RPA with BPA, organizations can achieve automation across their business processes. AgilePoint is a cross-functional BPA platform ideal for medium to large enterprises to rescue their RPA investments.
What are the three main business processes that BPA tools can help automate?
You can use process automation tools to automate three types of business processes.
- Core: These are cross-functional business processes unique to each organization and generate the most value.
- Management: These processes are related to monitoring, control, and corporate governance of a company.
- Support: These processes support the core processes. For instance, a defense equipment firm’s HR processes may be termed as support processes.
Resources
List of additional resources to help you learn more about Business Process Automation.
- The Role of Automation in Digital Transformation
- Three Major Differences Between Workflow Automation & Business Process Automation
- Why Business Process Automation Is A Must For Your Organization
- Three Ways Mining Companies are Using Business Process Automation
Discover how AgilePoint Business Process Automation software can help your business by
requesting a personalized demonstration today! After your free personalized demo, you can choose a plan that best suits your organization's needs.
Are you ready to reengineer your business
automation processes?

A modern process automation and orchestration platform that enables you to open up and seize new business opportunities, supercharge innovation, unlock new levels of efficiency and productivity, and deliver the experiences that help you win.
Follow Us
Platform

Automate business processes and workflows at scale. AgilePoint helps enterprises democratize and accelerate digital transformation, reduce technical debt and future-proof ROI.
Resources
© 2023 AgilePoint. All rights reserved.